iOS之Runtime
动态语言VS静态语言
动态语言(如Python、Ruby、JavaScript)和静态语言(如C、C++、Java、Swift)是一个和语言对应编译器相关的概念,主要的区别在于类型系统和方法调用上,比如一个JS变量可以随意设置类型而不会报错。
OC是动态性语言,区别于静态语言,动态语言在编译后的方法调用,不是编译后就固定了。而是采用了一套动态检索的机制,另外runtime API能够编辑这些元数据。
Runtime API
类的结构
类对象(Class)是由程序员定义并在运行时由编译器创建的,它没有自己的实例变量,这里需要注意的是类的成员变量和实例方法列表是属于实例对象的,但其存储于类对象当中的。
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
struct objc_class {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
#if !__OBJC2__
Class _Nullable super_class OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
const char * _Nonnull name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long version OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long info OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
long instance_size OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_ivar_list * _Nullable ivars OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_method_list * _Nullable * _Nullable methodLists OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_cache * _Nonnull cache OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
struct objc_protocol_list * _Nullable protocols OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
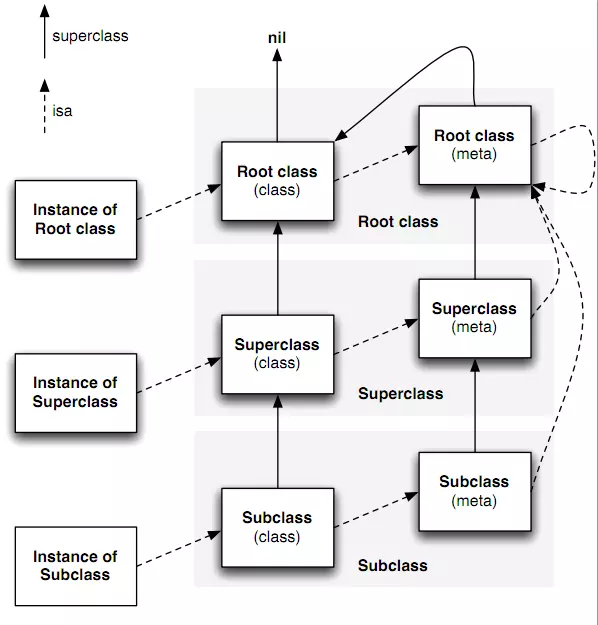
- isa:是Objc对象的isa指针指向的是类对象。类对象包含isa和superclass指针,它们的isa指向的是metaclass,它们的superclass指向父类。metaclass的isa指向它的基类;
- cache:用于缓存最近使用的方法。一个接收者对象接收到一个消息时,它会根据isa指针去查找能够响应这个消息的对象。在实际使用中,这个对象只有一部分方法是常用的,很多方法其实很少用或者根本用不上。这种情况下,如果每次消息来时,我们都是methodLists中遍历一遍,性能势必很差。这时,cache就派上用场了。在我们每次调用过一个方法后,这个方法就会被缓存到cache列表中,下次调用的时候runtime就会优先去cache中查找,如果cache没有,才去methodLists中查找方法。这样,对于那些经常用到的方法的调用,但提高了调用的效率。
获取类名
const char * class_getName ( Class cls );
动态创建类
// 创建一个新类和元类
Class objc_allocateClassPair ( Class superclass, const char *name, size_t extraBytes ); //如果创建的是root class,则superclass为Nil。extraBytes通常为0
// 销毁一个类及其相关联的类
void objc_disposeClassPair ( Class cls ); //在运行中还存在或存在子类实例,就不能够调用这个。
// 在应用中注册由objc_allocateClassPair创建的类
void objc_registerClassPair ( Class cls ); //创建了新类后,然后使用class_addMethod,class_addIvar函数为新类添加方法,实例变量和属性后再调用这个来注册类,再之后就能够用了。
对象
实例对象是我们对类对象alloc或者new操作时所创建的,在这个过程中会拷贝实例所属的类的成员变量,但并不拷贝类定义的方法。对象最重要的是可以给其发送消息,调用实例方法时,系统会根据实例的isa指针去类的方法列表及父类的方法列表中寻找与消息对应的selector指向的方法。
/// Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object {
Class _Nonnull isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
};
对对象的类操作
// 返回给定对象的类名
const char * object_getClassName ( id obj );
// 返回对象的类
Class object_getClass ( id obj );
// 设置对象的类
Class object_setClass ( id obj, Class cls );
获取对象的类定义
// 获取已注册的类定义的列表
int objc_getClassList ( Class *buffer, int bufferCount );
// 创建并返回一个指向所有已注册类的指针列表
Class * objc_copyClassList ( unsigned int *outCount );
// 返回指定类的类定义
Class objc_lookUpClass ( const char *name );
Class objc_getClass ( const char *name );
Class objc_getRequiredClass ( const char *name );
// 返回指定类的元类
Class objc_getMetaClass ( const char *name );
动态创建对象
// 创建类实例
id class_createInstance ( Class cls, size_t extraBytes ); //会在heap里给类分配内存。这个方法和+alloc方法类似。
// 在指定位置创建类实例
id objc_constructInstance ( Class cls, void *bytes );
// 销毁类实例
void * objc_destructInstance ( id obj ); //不会释放移除任何相关引用
Metaclass
元类(Metaclass)就是类对象的类,每个类都有自己的元类,也就是objc_class结构体里面isa指针所指向的类. Objective-C的类方法是使用元类的根本原因,因为其中存储着对应的类对象调用的方法即类方法。
属性
在Objective-C中,属性(property)和成员变量是不同的。那么,属性的本质是什么?它和成员变量之间有什么区别?简单来说属性是添加了存取方法的成员变量,也就是:@property = ivar + getter + setter;
//遍历获取所有属性Property
- (void) getAllProperty {
unsigned int propertyCount = 0;
objc_property_t *propertyList = class_copyPropertyList([Person class], &propertyCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < propertyCount; i++ ) {
objc_property_t *thisProperty = propertyList[i];
const char* propertyName = property_getName(*thisProperty);
NSLog(@"Person拥有的属性为: '%s'", propertyName);
}
}
objc_property_t & objc_property_attribute_t
/// An opaque type that represents an Objective-C declared property.
typedef struct objc_property *objc_property_t;
typedef struct {
const char * _Nonnull name; /**< The name of the attribute */
const char * _Nonnull value; /**< The value of the attribute (usually empty) */
} objc_property_attribute_t;
常用的属性如下:
- 属性类型 name值:T value:变化
- 编码类型 name值:C(copy) &(strong) W(weak)空(assign) 等 value:无
- 非/原子性 name值:空(atomic) N(Nonatomic) value:无
- 变量名称 name值:V value:变化
例如:
@interface person : NSObjec{
NSString *_name;
}
int main(){
objc_property_attribute_t nonatomic = {"N", ""};
objc_property_attribute_t strong = {"&", ""};
objc_property_attribute_t type = {"T", "@\"NSString\""};
objc_property_attribute_t ivar = {"V", "_name"};
objc_property_attribute_t attributes[] = {nonatomic, strong, type, ivar};
BOOL result = class_addProperty([person class], "name", attributes, 4);
}
操作函数
// 获取属性名
const char * property_getName ( objc_property_t property );
// 获取属性特性描述字符串
const char * property_getAttributes ( objc_property_t property );
// 获取属性中指定的特性
char * property_copyAttributeValue ( objc_property_t property, const char *attributeName );
// 获取属性的特性列表
objc_property_attribute_t * property_copyAttributeList ( objc_property_t property, unsigned int *outCount );
成员变量列表
objc_ivar_list
struct objc_ivar_list {
int ivar_count OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#ifdef __LP64__
int space OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
#endif
/* variable length structure */
struct objc_ivar ivar_list[1] OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
}
ivars是一个数组,数组中每个元素是指向Ivar(变量信息)的指针。
获取所有成员变量:
//遍历获取Person类所有的成员变量IvarList
- (void) getAllIvarList {
unsigned int methodCount = 0;
Ivar * ivars = class_copyIvarList([Person class], &methodCount);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < methodCount; i ++) {
Ivar ivar = ivars[i];
const char * name = ivar_getName(ivar);
const char * type = ivar_getTypeEncoding(ivar);
NSLog(@"Person拥有的成员变量的类型为%s,名字为 %s ",type, name);
}
free(ivars);
}
方法
Method 代表类中某个方法的类型
/// An opaque type that represents a method in a class definition.
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
objc_method 存储了方法名,方法类型和方法实现:
struct objc_method {
SEL _Nonnull method_name OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
char * _Nullable method_types OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
IMP _Nonnull method_imp OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
} OBJC2_UNAVAILABLE;
- 方法名类型为 SEL;
- 方法类型 method_types 是个 char 指针,存储方法的参数类型和返回值类型;
- method_imp 指向了方法的实现,本质是一个函数指针;
简言之,Method = SEL + IMP + method_types,相当于在SEL和IMP之间建立了一个映射。以下是Method操作方法:
// 调用指定方法的实现,返回的是方法实现时的返回,参数receiver不能为空,这个比method_getImplementation和method_getName快
id method_invoke ( id receiver, Method m, ... );
// 调用返回一个数据结构的方法的实现
void method_invoke_stret ( id receiver, Method m, ... );
// 获取方法名,希望获得方法明的C字符串,使用sel_getName(method_getName(method))
SEL method_getName ( Method m );
// 返回方法的实现
IMP method_getImplementation ( Method m );
// 获取描述方法参数和返回值类型的字符串
const char * method_getTypeEncoding ( Method m );
// 获取方法的返回值类型的字符串
char * method_copyReturnType ( Method m );
// 获取方法的指定位置参数的类型字符串
char * method_copyArgumentType ( Method m, unsigned int index );
// 通过引用返回方法的返回值类型字符串
void method_getReturnType ( Method m, char *dst, size_t dst_len );
// 返回方法的参数的个数
unsigned int method_getNumberOfArguments ( Method m );
// 通过引用返回方法指定位置参数的类型字符串
void method_getArgumentType ( Method m, unsigned int index, char *dst, size_t dst_len );
// 返回指定方法的方法描述结构体
struct objc_method_description * method_getDescription ( Method m );
// 设置方法的实现
IMP method_setImplementation ( Method m, IMP imp );
// 交换两个方法的实现
void method_exchangeImplementations ( Method m1, Method m2 );
操作函数
// 添加方法
BOOL class_addMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types ); //和成员变量不同的是可以为类动态添加方法。如果有同名会返回NO,修改的话需要使用method_setImplementation
// 获取实例方法
Method class_getInstanceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name );
// 获取类方法
Method class_getClassMethod ( Class cls, SEL name );
// 获取所有方法的数组
Method * class_copyMethodList ( Class cls, unsigned int *outCount );
// 替代方法的实现
IMP class_replaceMethod ( Class cls, SEL name, IMP imp, const char *types );
// 返回方法的具体实现
IMP class_getMethodImplementation ( Class cls, SEL name );
IMP class_getMethodImplementation_stret ( Class cls, SEL name );
// 类实例是否响应指定的selector
BOOL class_respondsToSelector ( Class cls, SEL sel );
消息转发流程
objc_msgSend
[array insertObject:foo atIndex:5];
// 等价
objc_msgSend(array, @selector(insertObject:atIndex:), foo, 5);
- 首先检查这个selector是不是要忽略;
- 检测这个selector的target是不是nil,OC允许我们对一个nil对象执行任何方法不会Crash,因为运行时会被忽略掉;
- 如果上面两步都通过了,就开始查找这个类的实现IMP,先从cache里查找,如果找到了就运行对应的函数去执行相应的代码;
- 如果cache中没有找到就找类的方法列表中是否有对应的方法;
- 如果类的方法列表中找不到就到父类的方法列表中查找,一直找到NSObject类为止;
- 如果还是没找到就要开始进入动态方法解析和消息转发;
动态方法解析:
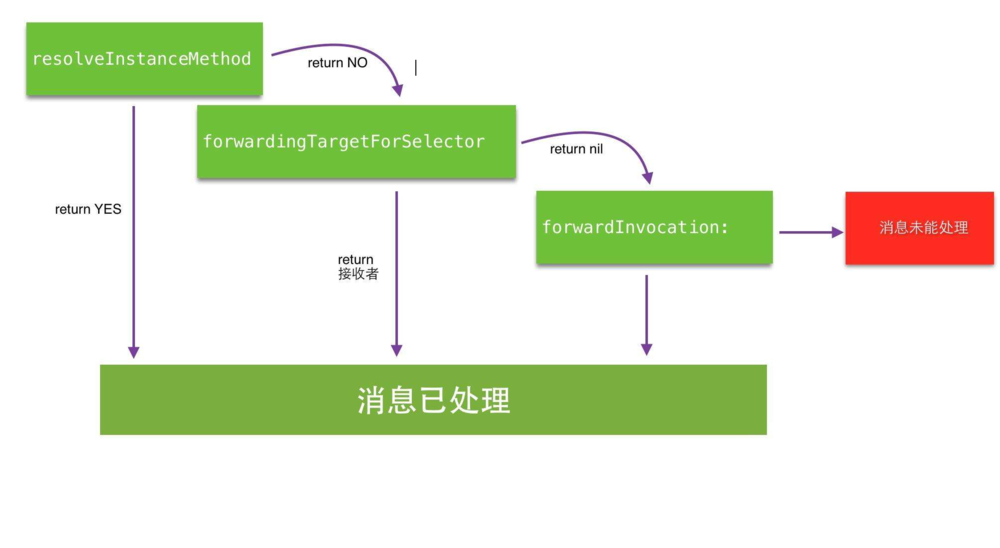
没有方法的实现,程序会在运行时挂掉并抛出 unrecognized selector sent to … 的异常。但在异常抛出前,Objective-C 的运行时会给你三次拯救程序的机会:
- Method resolution
- Fast forwarding
- Normal forwarding
- Runtime 发送 +resolveInstanceMethod: 或者 +resolveClassMethod: 尝试去 resolve 这个消息;
- 如果 resolve 方法返回 NO,Runtime 就发送 -forwardingTargetForSelector: 允许你把这个消息转发给另一个对象;
- 如果没有新的目标对象返回, Runtime 就会发送-methodSignatureForSelector: 和 -forwardInvocation: 消息。你可以发送 -invokeWithTarget: 消息来手动转发消息或者发送 -doesNotRecognizeSelector: 抛出异常。
应用:防止程序崩溃机制;
应用
- Associate用来给instance加变量的方式,Method swizzling实现hook(插入编程),自实现block型kvo和notificationcenter
- KVO的实现,自动生成了子类,isa指向子类,子类重写setter方法。所以如果自定义了setter方法,kvo会失效的,解决方法是在实现文件中@dynamic一下。
