有时候用网页展示一大片图文效果不怎么好,这时候就有必要用CoreText框架实现页面渲染了;
CoreText重要的几个元素
- CTFramesetterRef
- CTFrameRef
- CTLineRef
- CTRunRef
CTFrame 作为一个整体的画布(Canvas),其中由行(CTLine)组成,而每行可以分为一个或多个小方块(CTRun)。
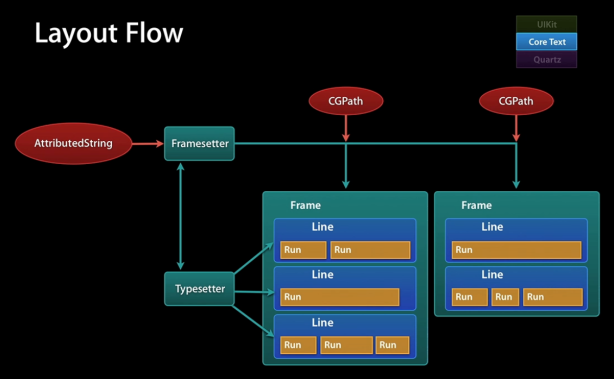
一般流程
使用core text就是先有一个要显示的string,然后定义这个string每个部分的样式->attributedString -> 生成 CTFramesetter -> 得到CTFrame -> 绘制(CTFrameDraw);
细节
- DisplayView继承子UIView,重写[drawRect:]方法。该方法通过传入的CTFrameRef,然后通过CTFrameDraw(self.data.ctFrame, context)就显示完毕;
- 自定义一个Parser把接口数据转换成包含CTFrameRef的CoreTextData的对象,解析过程如下:
- 创建AttributeString,这一步最关键;
- 根据AttributeString创建CTFramesetterRef实例;
- 根据CTFramesetterRef获取绘制高度;
- 根据CTFramesetterRef获取CTFrameRef;
- 将生成好的CTFrameRef实例和计算好的绘制高度保存到CoreTextData实例中,最后返回CoreTextData实例;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| + (CoreTextData *)parseAttributedContent:(NSAttributedString *)content config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
// 创建CTFramesetterRef实例
CTFramesetterRef framesetter = CTFramesetterCreateWithAttributedString((CFAttributedStringRef)content);
// 获得要绘制的区域的高度
CGSize restrictSize = CGSizeMake(config.width, CGFLOAT_MAX);
CGSize coreTextSize = CTFramesetterSuggestFrameSizeWithConstraints(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0,0), nil, restrictSize, nil);
CGFloat textHeight = coreTextSize.height;
// 生成CTFrameRef实例
CTFrameRef frame = [self createFrameWithFramesetter:framesetter config:config height:textHeight];
// 将生成好的CTFrameRef实例和计算好的绘制高度保存到CoreTextData实例中,最后返回CoreTextData实例
CoreTextData *data = [[CoreTextData alloc] init];
data.ctFrame = frame;
data.height = textHeight;
data.content = content;
// 释放内存
CFRelease(frame);
CFRelease(framesetter);
return data;
}
+ (CTFrameRef)createFrameWithFramesetter:(CTFramesetterRef)framesetter
config:(CTFrameParserConfig *)config
height:(CGFloat)height {
CGMutablePathRef path = CGPathCreateMutable();
CGPathAddRect(path, NULL, CGRectMake(0, 0, config.width, height));
CTFrameRef frame = CTFramesetterCreateFrame(framesetter, CFRangeMake(0, 0), path, NULL);
CFRelease(path);
return frame;
}
|
注意事项
如果光是文本确实没什么好说的,但是加入了图片、链接、选中、选中menu、点击图片手势等细节之后很多地方有点费劲;
- 图片的填充,在生成Attributestr的时候,根据接口来的array数据遍历append;如果其中的一个元素是图片,就创建空白占位符,并且设置它的CTRunDelegate信息,如果给CTRun设置了CTRunDelegateRef属性框架,在渲染CTRun的时候会调用设置的delegate获取decent、ascent、width等信息用来绘制。FrameRef创建好之后,遍历FrameRef的line以及line中的run初始化imageData.imagePosition,在最终drawrect的时候调用CGContextDrawImage(context, imageData.imagePosition, image.CGImage)就能够显示图片;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
static CGFloat ascentCallback(void *ref){
CGFloat picWidth = [[(__bridge NSDictionary *)ref objectForKey:@"width"] floatValue];
CGFloat picHeight = [[(__bridge NSDictionary *)ref objectForKey:@"height"] floatValue];
CGFloat height = defaultConfig.width/(picWidth/picHeight);
return height;
}
static CGFloat descentCallback(void *ref){
return 0;
}
static CGFloat widthCallback(void* ref){
return defaultConfig.width;
}
+ (NSAttributedString *)parseImageDataFromNSDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict
config:(CTFrameParserConfig*)config {
CTRunDelegateCallbacks callbacks;
memset(&callbacks, 0, sizeof(CTRunDelegateCallbacks));
callbacks.version = kCTRunDelegateVersion1;
callbacks.getAscent = ascentCallback;
callbacks.getDescent = descentCallback;
callbacks.getWidth = widthCallback;
CTRunDelegateRef delegate = CTRunDelegateCreate(&callbacks, (__bridge void *)(dict));
// 使用0xFFFC作为空白的占位符
unichar objectReplacementChar = 0xFFFC;
NSString * content = [NSString stringWithCharacters:&objectReplacementChar length:1];
NSDictionary * attributes = [self attributesWithConfig:config withContentTypeStr:@"pic"];
NSMutableAttributedString * space = [[NSMutableAttributedString alloc] initWithString:content
attributes:attributes];
CFAttributedStringSetAttribute((CFMutableAttributedStringRef)space, CFRangeMake(0, 1),
kCTRunDelegateAttributeName, delegate);
CFRelease(delegate);
return space;
}
|
- 通过上一步设置好占位符初始化好CTFrameRef之后,再遍历整个CTFrameRef的line,通过(NSArray *)CTLineGetGlyphRuns(line)获取每一行的CTRunDelegateRef,调用之前设置好的delegate方法,设置好image的显示的rect;
- CoreTextImageData的imagePosition属性; // 此坐标是CoreText的坐标系,而不是UIKit的坐标系;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| for (int i = 0; i < lineCount; ++i) {
if (imageData == nil) {
break;
}
CTLineRef line = (__bridge CTLineRef)lines[i];
NSArray * runObjArray = (NSArray *)CTLineGetGlyphRuns(line);
for (id runObj in runObjArray) {
CTRunRef run = (__bridge CTRunRef)runObj;
NSDictionary *runAttributes = (NSDictionary *)CTRunGetAttributes(run);
CTRunDelegateRef delegate = (__bridge CTRunDelegateRef)[runAttributes valueForKey:(id)kCTRunDelegateAttributeName];
if (delegate == nil) {
continue;
}
NSDictionary * metaDic = CTRunDelegateGetRefCon(delegate);
if (![metaDic isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
continue;
}
CGRect runBounds;
CGFloat ascent;
CGFloat descent;
runBounds.size.width = CTRunGetTypographicBounds(run, CFRangeMake(0, 0), &ascent, &descent, NULL);
runBounds.size.height = ascent + descent;
CGFloat xOffset = CTLineGetOffsetForStringIndex(line, CTRunGetStringRange(run).location, NULL);
runBounds.origin.x = lineOrigins[i].x + xOffset;
runBounds.origin.y = lineOrigins[i].y;
runBounds.origin.y -= descent;
CGPathRef pathRef = CTFrameGetPath(self.ctFrame);
CGRect colRect = CGPathGetBoundingBox(pathRef);
CGRect delegateBounds = CGRectOffset(runBounds, colRect.origin.x, colRect.origin.y);
imageData.imagePosition = delegateBounds;
imgIndex++;
if (imgIndex == self.imageArray.count) {
imageData = nil;
break;
} else {
imageData = self.imageArray[imgIndex];
}
}
}
|

